Dr Bev Brown Beverley.Brown@nottingham.ac.uk
CLINICAL TRIAL MANAGER
A Neural Basis for Contagious Yawning
Brown, Beverley J.; Kim, Soyoung; Saunders, Hannah; Bachmann, Clarissa; Thompson, Jessica; Ropar, Danielle; Jackson, Stephen R.; Jackson, Georgina M.
Authors
Soyoung Kim
Hannah Saunders
Clarissa Bachmann
Jessica Thompson
Professor DANIELLE ROPAR DANIELLE.ROPAR@NOTTINGHAM.AC.UK
PROFESSOR OF PSYCHOLOGY
Professor STEPHEN JACKSON stephen.jackson@nottingham.ac.uk
PROFESSOR OF COGNITIVE NEUROSCIENCE
Georgina M. Jackson
Abstract
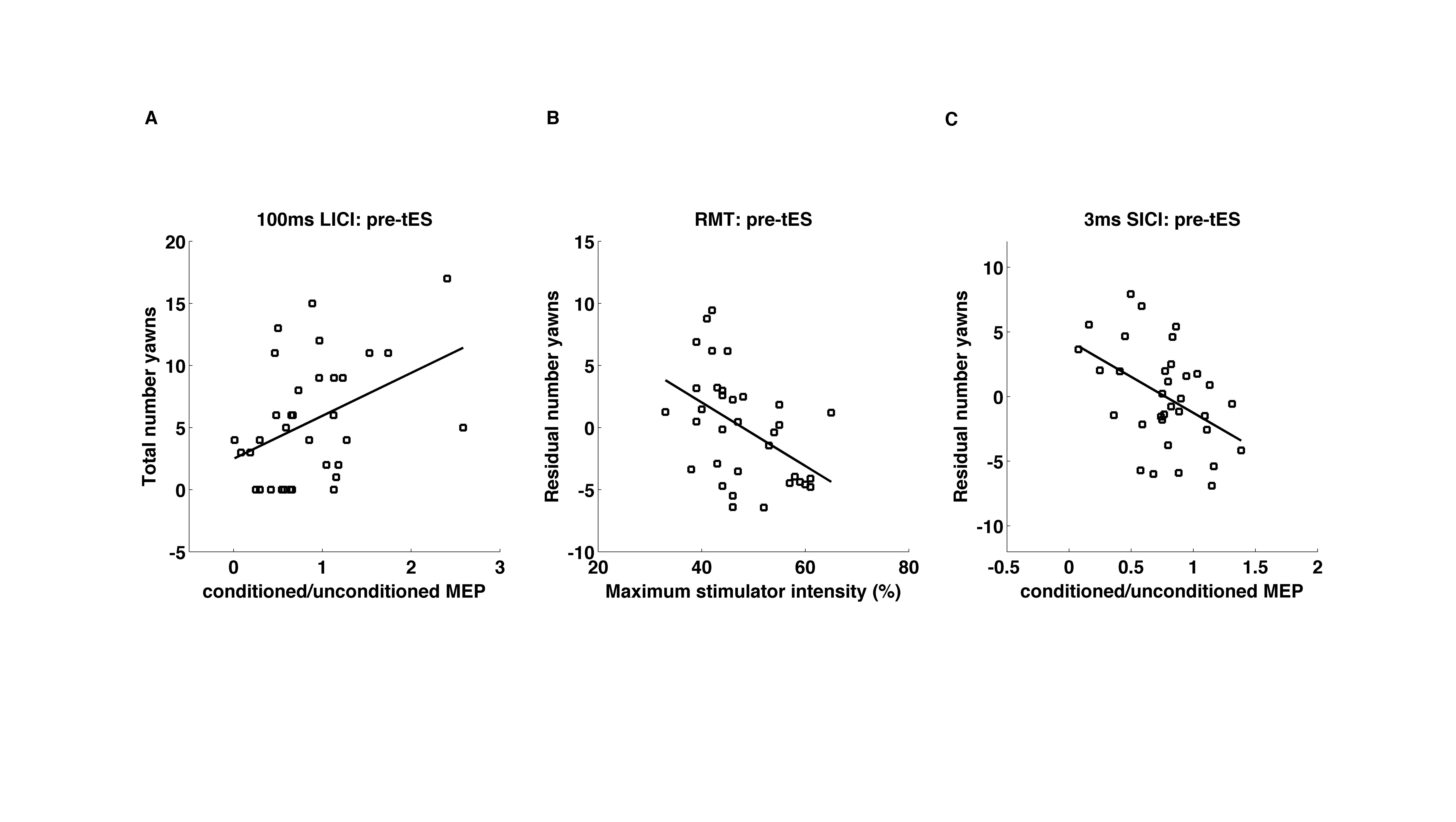
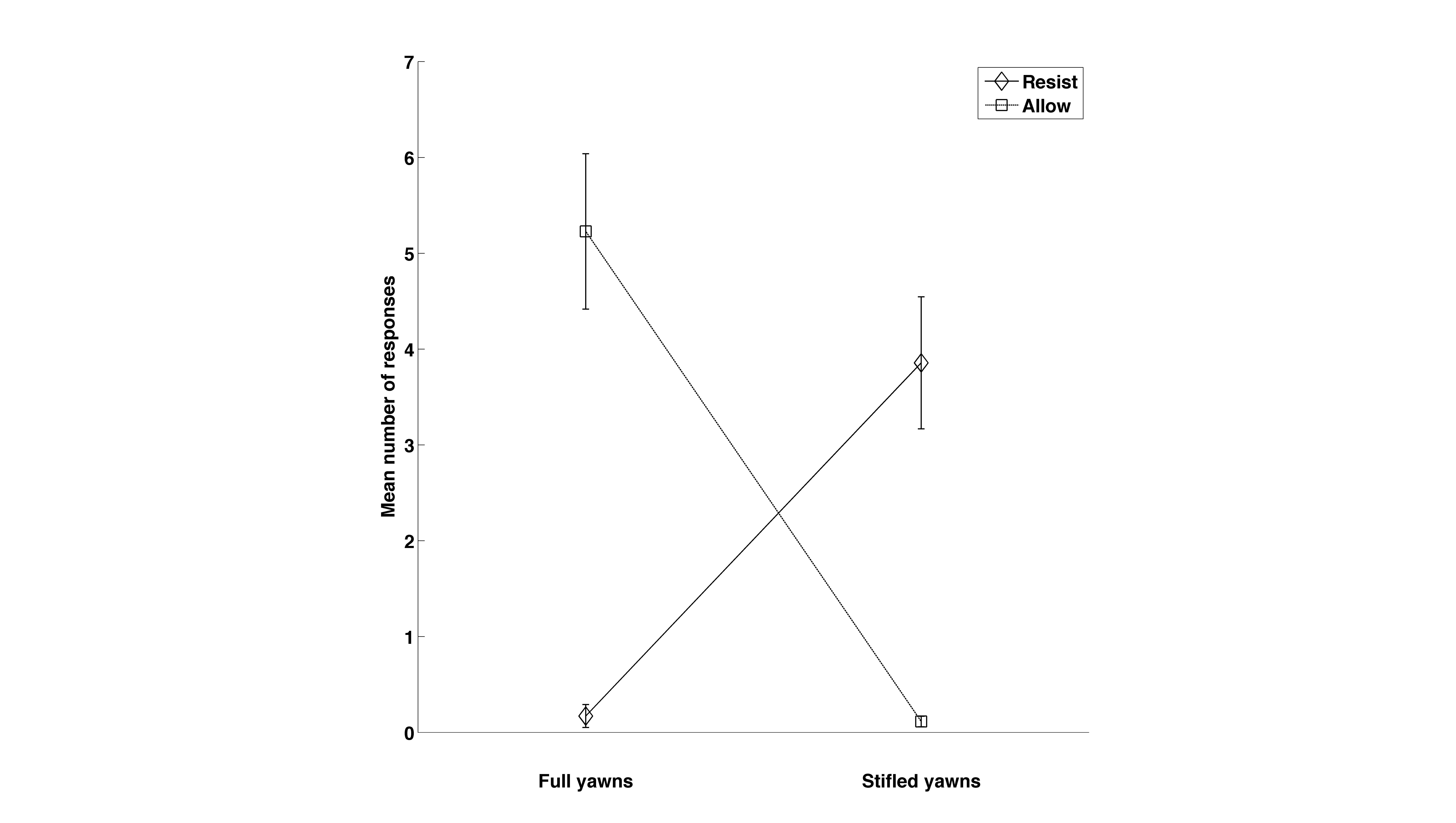
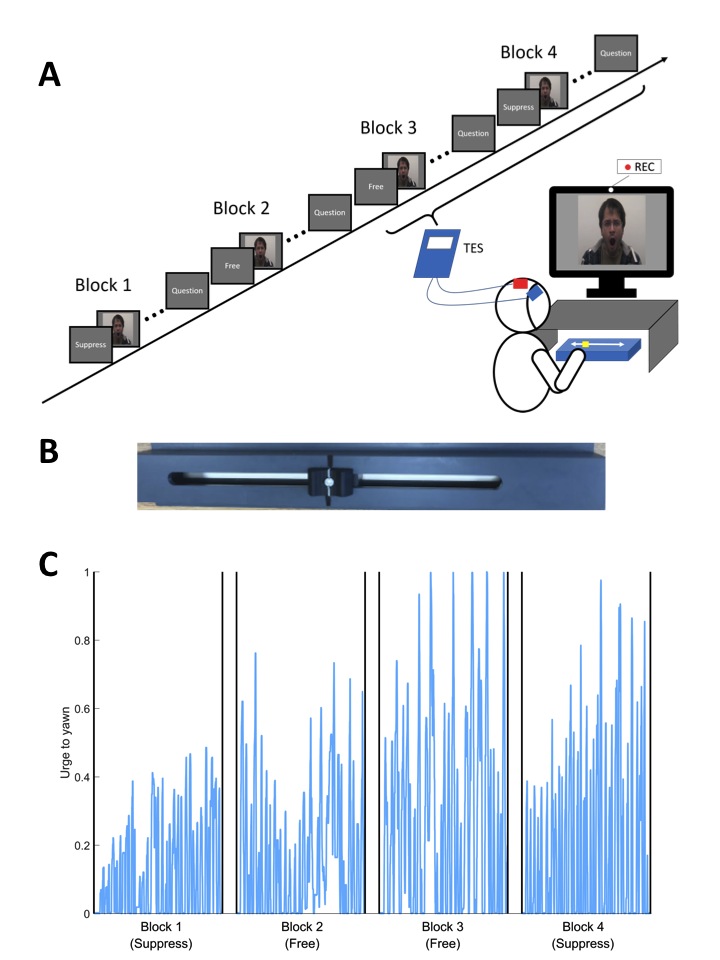
Contagious yawning, in which yawning is triggered involuntarily when we observe another person yawn, is a common form of echophenomena—the automatic imitation of another’s words (echolalia) or actions (echopraxia) [1]. The neural basis for echophenomena is unknown; however, it has been proposed that it is linked to disinhibition of the human mirror-neuron system [1–4 ] and hyper-excitability of cortical motor areas [ 1 ]. We investigated the neural basis for contagious yawning using transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). Thirty-six adults viewed video clips that showed another individual yawning and, in separate blocks, were instructed to either resist yawning or allow themselves to yawn. Participants were videoed throughout and their yawns or stifled yawns were counted. We used TMS to quantify motor cortical excitability and physiological inhibition for each participant, and these measures were then used to predict the propensity for contagious yawning across participants. We demonstrate that instructions to resist yawning increase the urge to yawn and alter how yawns are expressed (i.e., full versus stifled yawns) but do not alter the individual propensity for contagious yawning. By contrast, TMS measures of cortical excitability and physiological inhibition were significant predictors of contagious yawning and accounted for approximately 50% of the variability in contagious yawning. These data demonstrate that individual variability in the propensity for contagious yawning is determined by cortical excitability and physiological inhibition in the primary motor cortex.
Citation
Brown, B. J., Kim, S., Saunders, H., Bachmann, C., Thompson, J., Ropar, D., Jackson, S. R., & Jackson, G. M. (2017). A Neural Basis for Contagious Yawning. Current Biology, 27(17), 2713-2717.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.07.062
| Journal Article Type | Article |
|---|---|
| Acceptance Date | Jul 27, 2017 |
| Online Publication Date | Aug 31, 2017 |
| Publication Date | Sep 11, 2017 |
| Deposit Date | Jul 28, 2017 |
| Publicly Available Date | Sep 1, 2018 |
| Journal | Current Biology |
| Print ISSN | 0960-9822 |
| Electronic ISSN | 1879-0445 |
| Publisher | Cell Press |
| Peer Reviewed | Peer Reviewed |
| Volume | 27 |
| Issue | 17 |
| Pages | 2713-2717.e2 |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.07.062 |
| Keywords | Contagious yawning; Echophenomena; Transcranial magnetic stimulation [TMS]; Tourette syndrome; Motor cortex |
| Public URL | https://nottingham-repository.worktribe.com/output/881728 |
| Publisher URL | http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0960982217309661 |
| Additional Information | This article is maintained by: Elsevier; Article Title: A Neural Basis for Contagious Yawning; Journal Title: Current Biology; CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.07.062; Content Type: article; Copyright: © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd. |
| Contract Date | Jul 28, 2017 |
Files
1-s2.0-S0960982217309661-main
(1 Mb)
PDF
Publisher Licence URL
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.5/
Echo2 Fig 3.jpg
(1.4 Mb)
Image
Copyright Statement
Copyright information regarding this work can be found at the following address: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0
Echo2 Fig 2.jpg
(1.2 Mb)
Image
Copyright Statement
Copyright information regarding this work can be found at the following address: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0
Fig 1.jpg
(115 Kb)
Image
Copyright Statement
Copyright information regarding this work can be found at the following address: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0
Brown et al. CB 3rd revision text only.pdf
(176 Kb)
PDF
Copyright Statement
Copyright information regarding this work can be found at the following address: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0
You might also like
Policy Brief: Autism and Policing
(2024)
Report
Policy Brief: Neurodiversity in the workplace
(2024)
Report
Prevalence of Victimisation in Autistic Individuals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
(2022)
Journal Article
Downloadable Citations
About Repository@Nottingham
Administrator e-mail: discovery-access-systems@nottingham.ac.uk
This application uses the following open-source libraries:
SheetJS Community Edition
Apache License Version 2.0 (http://www.apache.org/licenses/)
PDF.js
Apache License Version 2.0 (http://www.apache.org/licenses/)
Font Awesome
SIL OFL 1.1 (http://scripts.sil.org/OFL)
MIT License (http://opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.html)
CC BY 3.0 ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/)
Powered by Worktribe © 2025
Advanced Search