Dr CHARLOTTE HALL CHARLOTTE.HALL@NOTTINGHAM.AC.UK
PRINCIPAL RESEARCH FELLOW
The clinical utility of QbTest in supporting the assessment and monitoring of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): What do paediatricians need to know?
Hall, Charlotte L; Bellato, Alessio; Kirk, Julie D; Hollis, Chris
Authors
Alessio Bellato
Julie D Kirk
Professor CHRIS HOLLIS chris.hollis@nottingham.ac.uk
PROFESSOR OF CHILD AND ADOLESCENT PSYCHIATRY AND DIGITAL MENTAL HEALTH
Abstract
The assessment of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) typically relies on subjective observer reports from parents, teachers, or the young person, combined with clinical observation and history. Children and young people often experience lengthy delays to assessment and medication initiation resulting from conflicting or missing observer reports and diagnostic uncertainty. However, more recently, a computerised test of attention, impulsivity and activity (QbTest) has been implemented as an adjunct to standard clinical practice, with the aim to provide a more objective measure of ADHD symptoms. Here, we discuss the evidence for the clinical utility of QbTest to aid in the assessment and monitoring of ADHD. Drawing on key literature and real-world case studies, we show the potential benefits that QbTest may have in creating service efficiencies for ADHD care, but also note limitations in diagnostic accuracy, importantly demonstrating that QbTest should supplement and not replace standard care. We review key barriers and facilitators to implementation, to aid decision making and planning in how to integrate QbTest in paediatric services.
Citation
Hall, C. L., Bellato, A., Kirk, J. D., & Hollis, C. (2023). The clinical utility of QbTest in supporting the assessment and monitoring of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): What do paediatricians need to know?. Paediatrics and Child Health, 33(9), 259-264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paed.2023.06.006
| Journal Article Type | Article |
|---|---|
| Acceptance Date | Feb 23, 2023 |
| Online Publication Date | Jul 18, 2023 |
| Publication Date | 2023-09 |
| Deposit Date | Feb 24, 2023 |
| Publicly Available Date | Jul 19, 2024 |
| Journal | Paediatrics and Child Health |
| Print ISSN | 1751-7222 |
| Electronic ISSN | 1878-206X |
| Publisher | Elsevier |
| Peer Reviewed | Peer Reviewed |
| Volume | 33 |
| Issue | 9 |
| Pages | 259-264 |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paed.2023.06.006 |
| Keywords | Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; ADHD; QbTest; diagnosis; assessment; monitoring; continuous performance test |
| Public URL | https://nottingham-repository.worktribe.com/output/17663940 |
| Publisher URL | https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1751722223001051 |
| Additional Information | This article is maintained by: Elsevier; Article Title: The clinical utility of QbTest in supporting the assessment and monitoring of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): what do paediatricians need to know?; Journal Title: Paediatrics and Child Health; CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paed.2023.06.006 |
Files
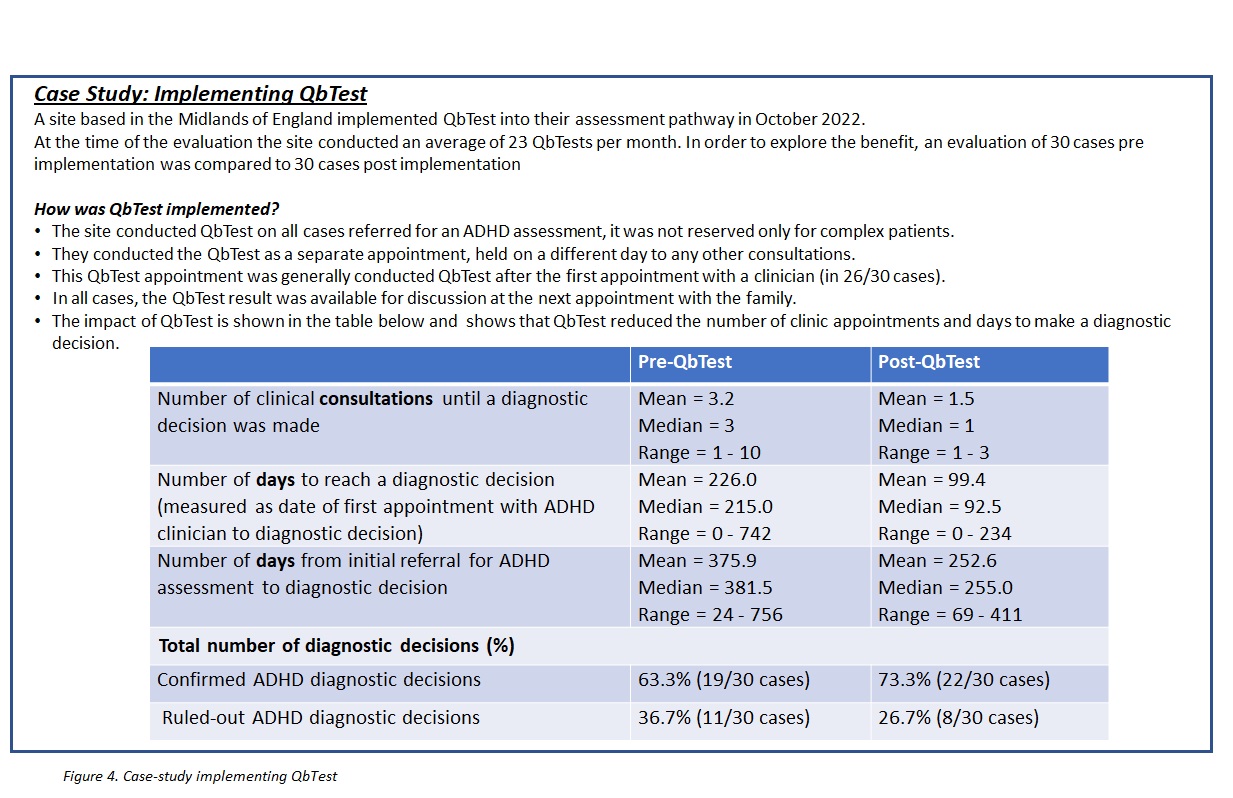
Figure 4 - Case study example
(331 Kb)
Image
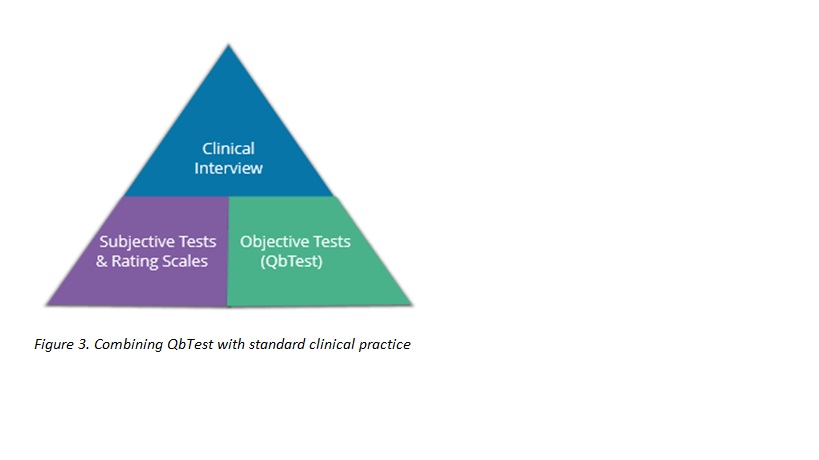
Figure 3 - adding QbTest to practice
(27 Kb)
Image
Figure 2a & 2b - pre and post meds
(168 Kb)
Image
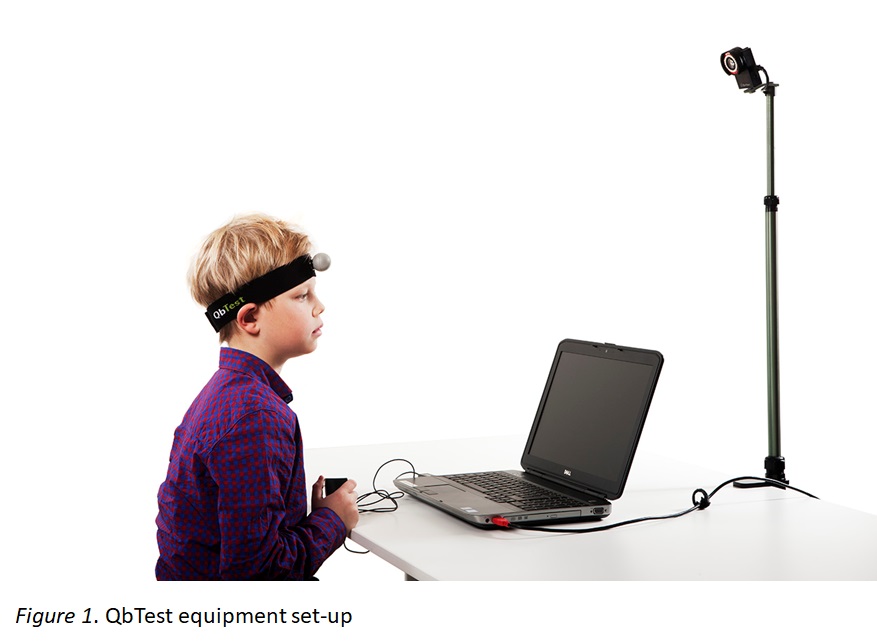
Figure 1 - QbTest equipment set-up
(69 Kb)
Image
QbTest Peds Paper - V3.1 18 Jan 23
(155 Kb)
PDF
You might also like
The impacts associated with having ADHD: an umbrella review
(2024)
Journal Article
Downloadable Citations
About Repository@Nottingham
Administrator e-mail: discovery-access-systems@nottingham.ac.uk
This application uses the following open-source libraries:
SheetJS Community Edition
Apache License Version 2.0 (http://www.apache.org/licenses/)
PDF.js
Apache License Version 2.0 (http://www.apache.org/licenses/)
Font Awesome
SIL OFL 1.1 (http://scripts.sil.org/OFL)
MIT License (http://opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.html)
CC BY 3.0 ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/)
Powered by Worktribe © 2025
Advanced Search